Improve your special cargo loading and transportation
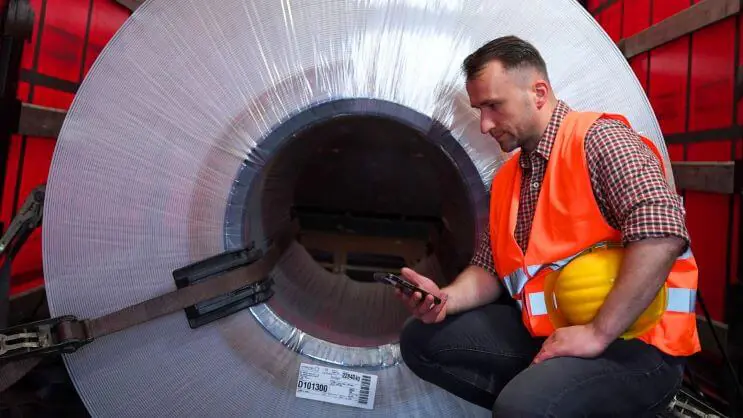

How do you handle special cargo?
What can you learn from this article?
Focusing on the constraints of special cargo handling, we want to emphasize the importance of compliance with shipping regulations. Understanding the challenges the logistics market faces today, we recognize that minor negligence in the transportation of goods can lead to serious accidents or result in costly fines for improper transportation.
In this article, we explain various ways of handling shipping with attention to special cargo. You can learn more about how to maintain the safety and distribution of various goods. Discover with us how to provide the best possible way to load and transport your special freight by using a software platform. Explore how your logistics, distribution, and transportation can benefit from easily accessible digital solutions.
How does special cargo work?
Carrying the cargo involves various modes of transport. We can ship our goods through air, road, rail, and sea. Most goods shipped globally or locally require specifications to protect them from loss. There are standardized ways of shipping that allow the delivery of unbroken shipments to the final customer. Some goods require special cargo, which implicates strict and dedicated shipping methods for certain types of cargo. Special cargo covers shipping goods or equipment that require special handling during transport. This is often related to non-standardized dimensions of the cargo, abnormal weight and size, or other material handling conditions. In the retail sector, such as the healthcare or food industry, we often consider special cargo items that require adherence to restricted temperature norms and loading. These norms help to prevent consignment against damage and waste. Also giving other examples of special freight, they may require strict care to ensure shipping is in accordance with regulations that protect the environment from pollution.

Here are the examples of goods that require special cargo:
IMO Cargo – Dangerous goods (DG)
IMO-classified cargo includes materials that have characteristics that would make them be considered dangerous goods. In this case, we can refer to goods such as chemicals or fuels. These will have different characteristics that require restricted provisions for transport (DGR), which are normalized by The International Air Transport Association (IATA). [1]
Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG)
FMCG goods require special handling due to their vulnerability to damage. The reason for damage often comes with too high of a temperature or poor loading methods. FMCG cargo is linked to the healthcare and food industries.

Vehicles
Vehicles require special transportation, but in this case, it will strictly be related to sea cargo. The ferry that is transporting several thousands of cars is exposed to dangerous fire conditions. In that case, vehicle hauling is very restricted, and it is considered a special cargo.
Special Equipment
Handling special equipment involves transporting goods that require unique and specific machinery to allow for safe and secure transport. These goods could include industrial machinery, components for windmill plants, manufacturing instruments, and tools used by heavy industries.
Raw Materials
Special cargo handling for raw materials is about the transportation of essential materials for manufacturing and production. This can also include materials dedicated to industrial needs related to securing the domestic energy sector (transport of charcoal, etc.). These materials often require specific conditions such as controlled temperatures, protective packaging, or specialized handling equipment.
Waste cargo
Waste cargo handling involves transporting materials that require special care due to their nature and potential environmental impact. This category includes hazardous waste, electronic waste (e-waste), or other materials that need adherence to strict disposal and recycling regulations.
Lithium batteries
Lithium batteries are a key component of various electronic devices. They require special attention during transportation, mostly because of their temperature sensitivity. There is a high possibility of short-circuiting and the risk of thermal runaway.

Special care for cargo needs to be taken for all of the given examples. Your business must address all of these needs with attention to how goods are loaded and handled during transport. Restrictions for loading and transportation of special cargo aren’t accidentally implemented. Some prior incidents clearly show that careless handling of goods during transit can cause tremendous accidents. One such example is the UPS Airlines Flight 6 cargo plane crash in 2010 in Dubai. The cause of the crash was believed to be the self-ignition of lithium-ion batteries carried in the cargo hold. There were 81,000 such batteries on board the aircraft. The reason for self-ignition was the poorly planned loading of the goods, where the close presence of many batteries began to emit high temperatures. [2]
How do you handle the shipment of dangerous goods?
Distribution in logistics combines the storage of various types of goods, impacting material handling in warehouses. Your business must use dedicated areas depending on the kind of goods stored. Storing materials such as dangerous goods (DG) often involves using cages with limited volumes for hazardous materials or substances to separate flammable items from other goods in the warehouse. DGs require the same handling as lithium batteries, which are often stored in refrigerators in warehouses to keep them cool and prevent fires.
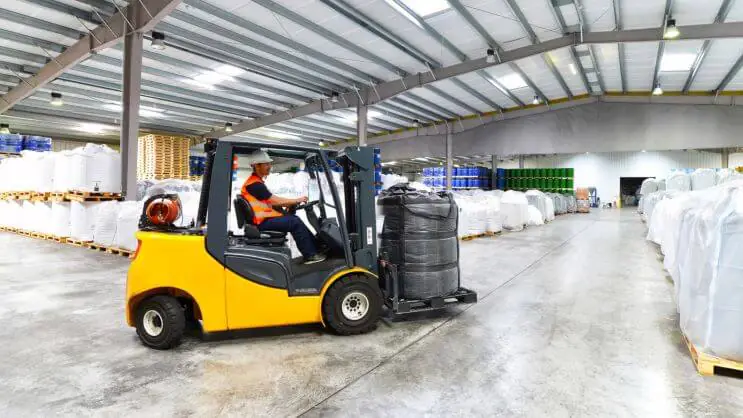

This brief explanation outlines DGs and lithium battery regulations in your warehouse. However, you not only need to deal with the challenges of storing these goods but also those related to properly shipping them.
Most of the DG special cargo is shipped with trailers. In this case, e-load planning refers to Less-Than-Load (LTL) shipping, as it is tough to predict if a single trailer will be fully loaded with only DGs. Here are the typical requirements for DGs – LTL loading:
- Before loading into a trailer or container, inspect the load. Do not load a damaged load or one that is not labeled properly.
- The loading trailer evenly distributes the load weight from side to side and end to end of the unit.
- Load the load at an even height, as far as the load allows.
- As a general rule, load a light load on top of a heavy load, using spacers if necessary.
- Load packages and containers of similar size in stacks.
- Use dividers between stacks of packages and containers of different sizes, types, or densities.
- Provide a stable base for all loads, whether palletized or individual items.
- Keep in mind the labeling of the DGs, as not all items can be loaded next to each other.
- Use a suitable bracing or dunnage (filler) material to maintain vertical alignment and prevent lateral movement.
The statistics in the Netherlands indicate that the highest volume of dangerous goods transported by road comprises fossil fuels such as diesel and petrol. This highlights the deliberate importance of considering what kind of transport requirements for DGs are crucial in some European countries. [3]
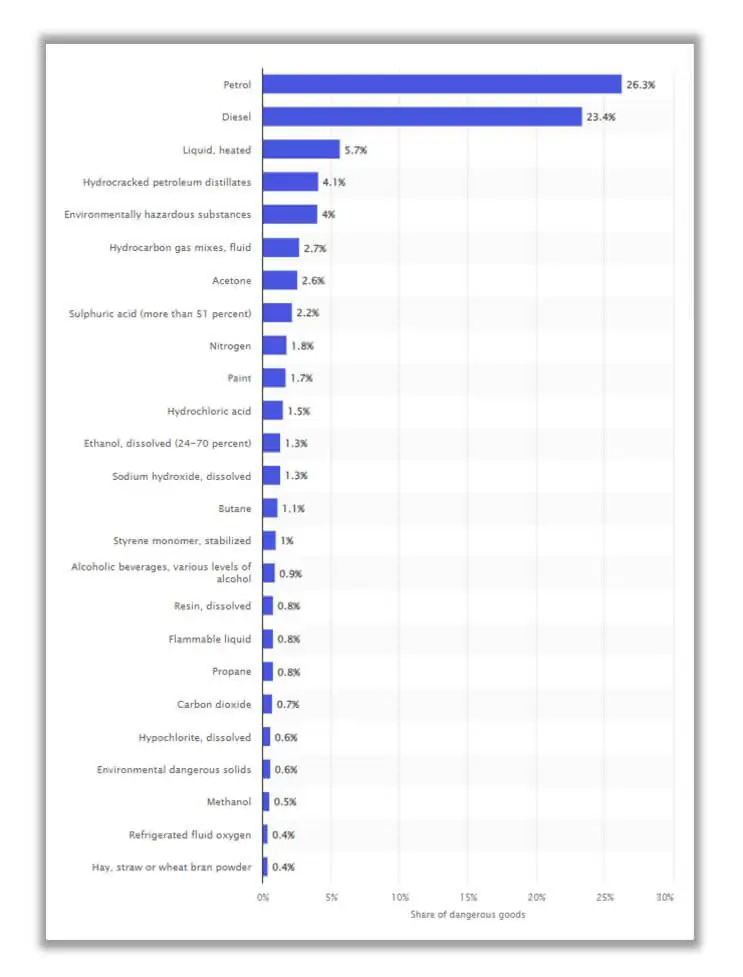
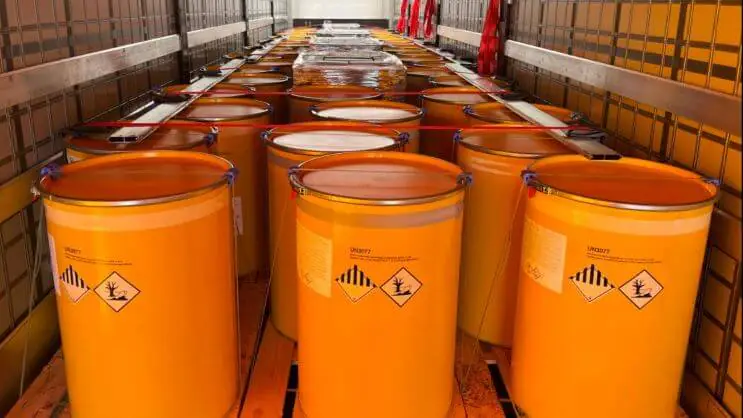
Depending on the transport mode and if you’re a freight forwarder, you may want to use road and air freight, where IATA regulations come into play. There are very restricted provisions that need to be followed to help airport staff understand how the shipment should be stored during transport. All items dedicated to shipping need to be properly labeled, providing indicators on how to load the goods correctly. Not following these regulations can cause your organization to pay expensive fines, as you may be convicted for exposing the entire cargo to danger. Sometimes, your shipment can be grounded at the airport and not delivered to your customer on time. Additional costs can also arise for exceeded storage time in the airport warehouse.
How do you prepare dangerous goods shipping?
Many guidelines should help load your cargo on the trailer properly and safely. Dealing with a high volume of Dangerous Goods daily, your operations can be exposed to errors. Warehouse clerks highly trained and certified by the IATA can find it difficult to cope with all of these restrictions and they may still encounter some issues, thus making mistakes caused by manual errors.

To prevent these errors, today’s companies are keen to digitize processes to simplify ways of handling and loading all freight. This approach helps companies follow the shipper’s printed directions and keep all of the loading patterns for specific shipments. One of the software solutions for effective load planning can be a platform that plans all loading for outbound trailers. Here are some of the features that are available from the loading platform for load-planning trailers and containers:
Setup cargo preferences
Inside the platform, you adjust loading parameters such as size, item positioning, placement, and rotation for each box in the calculated load plan.
Define your vehicles or containers
Determine the way of transport by using containers, pallets, trucks, trailers, and tractors with various axes.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) integrations
Platforms allow you to seamlessly integrate with most known ERP systems such as SAP, etc.
Reporting
You can create print reports from a visualized load plan, get better forecasting, share your load plans online, or even verify weight distribution compliance within permitted limits.
Step-by-step multi-cargo space load plan
You can plan several shipments upfront to save the time required to reconcile each outbound shipment separately.
How do you handle shipments for the FMCG industry?
Similar to DGs, the fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) industry also requires special cargo handling. Materials handled as FMCG require cooling storage and high attention to loading to avoid damage. Examples of FMCG products are medical products in the healthcare industry and perishables in the food industry. In both cases, goods must be delivered promptly and with a special way of handling. However, perishables can also be shipped over the ocean via air freight or through the ocean in containers which still require proper loading and shipping methods.
For this purpose, companies use trailers and containers with specially built systems that provide the required temperature to keep goods frozen or cooled inside. This is done to secure cargo against damages. This method applies all the way to the final destination of delivery regardless if the shipment will be forwarded by using various modes of transport, such as air freight, which is very popular along with road freight in planning supply chain solutions for special cargo.
Here are the important factors in protecting Perishable Foods for transport:
Refrigeration
Refrigeration is critical to maintaining food quality and extending shelf life by minimizing deterioration. Maintaining the ideal temperature during storage and distribution is key to preventing quality loss caused by both time and temperature.
Air circulation
Effective air circulation is essential to secure refrigerated cargo, ensure proper temperature maintenance, and prevent chilling or freezing injuries.
Trailer design
In trailer design, insulation is critical. Vehicles carrying perishable food products should have high-quality insulation, as measured by the U-factor. Plastic foams are commonly used because of their low U-factor, lightweight, water resistance, and lack of corrosion.
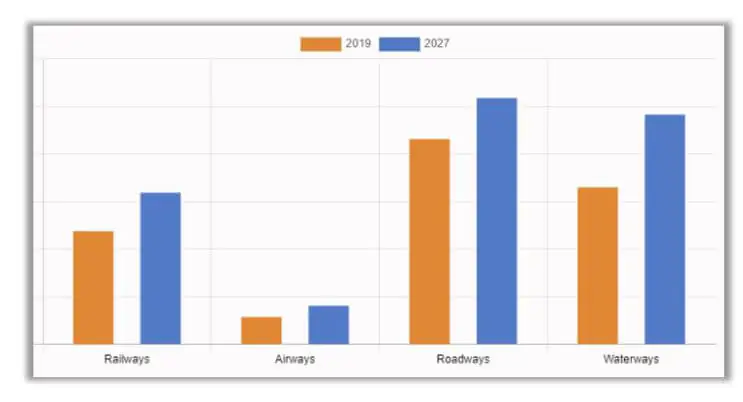
The FMCG logistics market provides a reference for using the transportation mode in FMCG. The waterway segment is predicted to be the most lucrative by 2027. By understanding which mode of transportation is predicted to be the most profitable in the future, we can better prepare for the outbound goods performance, which is closely related to truckload planning. [4]
Important loading patterns for Perishable Goods:
- Load cartons tightly from front to back and side wall to side wall of the vehicle.
- Stack cartons with top and bottom vents on top of each other so that the vents are aligned.
- Leave at least 10 cm (4 inches) of clearance between the top of the load and the ceiling to allow air to return to the refrigeration unit.
- Block off any clearances at the top of the T-rails at the rear of the vehicle so that air is pushed upward by the cargo.
- Load unit loads as tightly as possible.
- Cover the floor space not covered by unit loads with fiberboard or other suitable material to force air upward through the unit loads.
- Ensure that wood pallets or sheet floors have openings or slots to allow cooled air to flow into the unit load.
- Do not place the load so high that the air chutes are compressed and air circulation is blocked.
- For non-frozen loads, block the ends of pallets at the rear of the load to ensure that air pressure is maintained under the load.
Similar to DGs, FMCG goods such as perishables can be loaded on trucks more effectively by using a software platform dedicated to load planning. By using such a platform with a load plan, your business can benefit from the following:
Efficiency and a User-Friendly Interface
Most load planners maintain cargo items and results on a single screen. It eliminates the need to switch between tabs in the interface.
Time-Saving Load Planning
You can get access to a unique load planning algorithm that will help you quickly and effectively place cargo items into trucks and containers within seconds.
Optimal Use of Space
The software for load planning allows you to define or adjust your own cargo space. It contributes to optimal planning and space utilization.
Best 3D Visualization
It can provide you with the best 3D visualization of the entire load plan result. It offers your business an interactive view for detailed examination.
Integration Options for Convenience
Platforms for loading offer integration options via Application Programming Interface (API), Excel, and ERPs, such as SAP, for seamless data transfer and collaboration.
Cost-Saving Transportation Planning
You can calculate transportation costs and assess potential savings with efficient load planning capabilities.
Get an outlook on shipping and loading
Summarizing this article, we want to emphasize that there are several ways to handle special cargo goods for shipping. Regardless of the logistics and distribution method you are using, you are likely to encounter various loading issues caused by manual errors. To eliminate these issues, it is worth considering a platform for truckload planning.
EasyCargo provides your business with a load planner. With our platform, you can plan the shipping of your goods most suitably and safely. Do you want to know more about how to protect your special cargo while ensuring safe shipping and distribution? Try our platform for free and see how your daily operations can become easier.
References:
[1] IATA.org – https://www.iata.org
[2] UPS Airlines Flight 6 – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/UPS_Airlines_Flight_6
[3] Statista – https://www.statista.com/statistics/781450/road-transportation-of-dangerous-goods-in-the-netherlands/
[4] FMCG Logistics Market – https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/fmcg-logistics-market-A08768




